Nurturing Minds, Cultivating Futures: The Importance of Teaching Children About Food and Gardening
Introduction: Sowing the Seeds of Knowledge
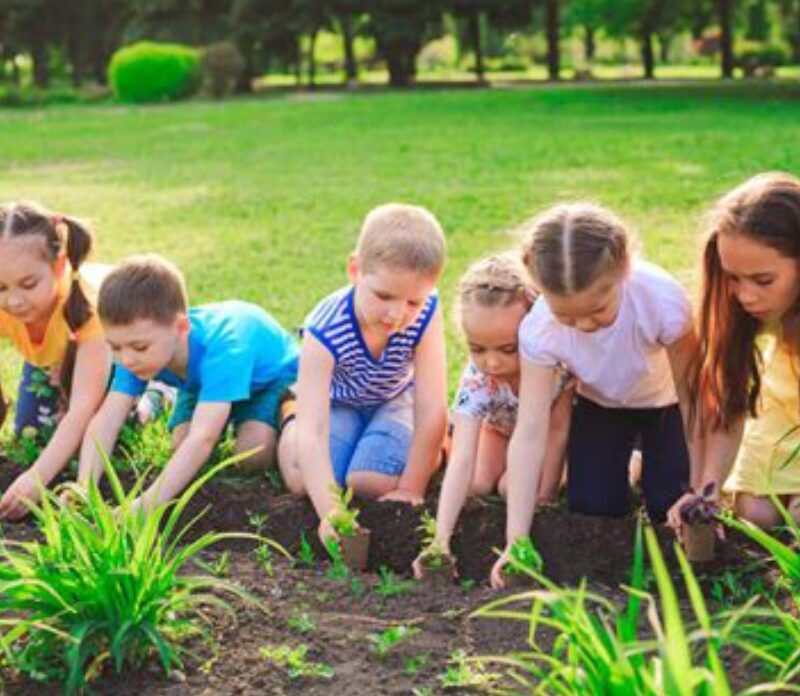
Understanding where our food comes from is more than just an educational exercise—it’s a foundational skill that fosters a deeper connection to nature, promotes healthier eating habits, and builds a sense of responsibility. Teaching children about the origins of their food through gardening is an investment in their future, equipping them with essential life skills and a greater appreciation for the environment. In this article, we explore the numerous benefits of integrating gardening into children’s education, from improving their nutritional choices to fostering sustainability and resilience.
The Benefits of Teaching Children About Food Origins
1. Encouraging Healthier Eating Habits
One of the most immediate benefits of teaching children about food origins is the impact it has on their diet. When children are actively involved in growing their own fruits and vegetables, they develop a sense of ownership and pride, making them more likely to eat nutritious foods. Research shows that children who participate in gardening programs consume more fresh produce and are more willing to try new foods.
Key Takeaways:
- Hands-on gardening fosters an appreciation for fresh, whole foods.
- Children who grow their own vegetables are more likely to eat them.
- Early exposure to gardening reduces picky eating habits.
2. Strengthening Environmental Awareness
By learning about food production, children gain a better understanding of the impact of agriculture on the planet. They learn about soil health, water conservation, and sustainable farming practices, helping them develop a sense of environmental stewardship. Gardening teaches the importance of reducing food waste, composting, and making eco-friendly choices.
Key Takeaways:
- Gardening connects children to nature and encourages sustainability.
- Hands-on learning promotes responsible environmental behaviors.
- Understanding food waste fosters better resource management.
3. Developing Essential Life Skills
Gardening isn’t just about growing plants—it’s about cultivating patience, resilience, and responsibility. Children who participate in gardening learn the value of hard work and delayed gratification, as they witness the gradual transformation of seeds into thriving plants. They also develop problem-solving skills when faced with challenges such as pests, weather changes, and soil conditions.
Key Takeaways:
- Gardening fosters patience and perseverance.
- Problem-solving skills are enhanced through real-world challenges.
- Taking care of plants instills a sense of responsibility.
Practical Ways to Integrate Gardening into Children’s Education
1. School and Community Gardens
Many schools and communities have started incorporating gardening programs into their curricula. School gardens provide hands-on learning experiences that complement science, nutrition, and environmental studies. Community gardens encourage teamwork, cooperation, and a sense of belonging.
Implementation Tips:
- Establish a dedicated gardening space in schools.
- Encourage students to participate in planting, watering, and harvesting.
- Use the garden as a platform for interdisciplinary learning.
2. Home Gardening for Families
Parents can easily integrate gardening into their daily routines by growing food at home. Whether it’s a small herb garden on a windowsill or a backyard vegetable patch, home gardening creates an interactive learning experience for children.
Implementation Tips:
- Start with easy-to-grow plants like tomatoes, basil, and lettuce.
- Involve children in every step, from planting to harvesting.
- Make gardening a fun family activity with rewards like “harvest day” meals.
3. Incorporating Technology and Online Learning
With advancements in technology, children can engage with gardening through virtual tools, mobile apps, and online resources. Augmented reality gardening apps, virtual field trips to farms, and interactive science experiments can enhance their learning experience.
Implementation Tips:
- Use gardening apps to track plant growth and learn about plant care.
- Watch online videos about farming, sustainability, and food production.
- Participate in virtual gardening workshops or community challenges.
The Connection Between Gardening and Mental Well-Being
In addition to physical health benefits, gardening has been proven to enhance mental well-being. The process of nurturing plants provides a sense of calm, reduces stress, and improves mood. Children who spend time outdoors in green spaces are more likely to experience lower levels of anxiety and higher levels of creativity.
Psychological Benefits:
- Gardening reduces stress and anxiety.
- Exposure to nature enhances mood and creativity.
- Hands-on activities improve focus and mindfulness.
The Long-Term Impact: Preparing Future Generations for Sustainability
By teaching children about gardening and food production today, we are preparing them for a future where sustainability is crucial. With increasing global concerns about food security and climate change, knowledge about growing food will become a valuable asset. The ability to cultivate one’s own food fosters self-sufficiency and resilience, ensuring future generations have the skills necessary to thrive in an ever-changing world.
Key Takeaways:
- Gardening education equips children with vital sustainability skills.
- Understanding food production fosters self-reliance and resilience.
- Future generations will be better prepared for environmental challenges.
Conclusion: Cultivating a Healthier Future
Teaching children about food origins through gardening is one of the most impactful ways to nurture their growth—both physically and intellectually. It empowers them to make healthier choices, appreciate the environment, and develop essential life skills. Whether through school programs, home gardens, or digital learning, the lessons learned in the garden extend far beyond the soil. Let’s invest in the future by cultivating young minds, one plant at a time.
Call to Action: Encourage your child to start a small garden today! Whether it’s a pot of herbs on the windowsill or a backyard vegetable patch, every step counts toward building a healthier, more sustainable future. Share your gardening experiences with us and inspire others to do the same! 🌱🥦🍎