Sustainable Aquaponics: Harnessing Solar Energy for a Self-Sufficient Food System
Introduction
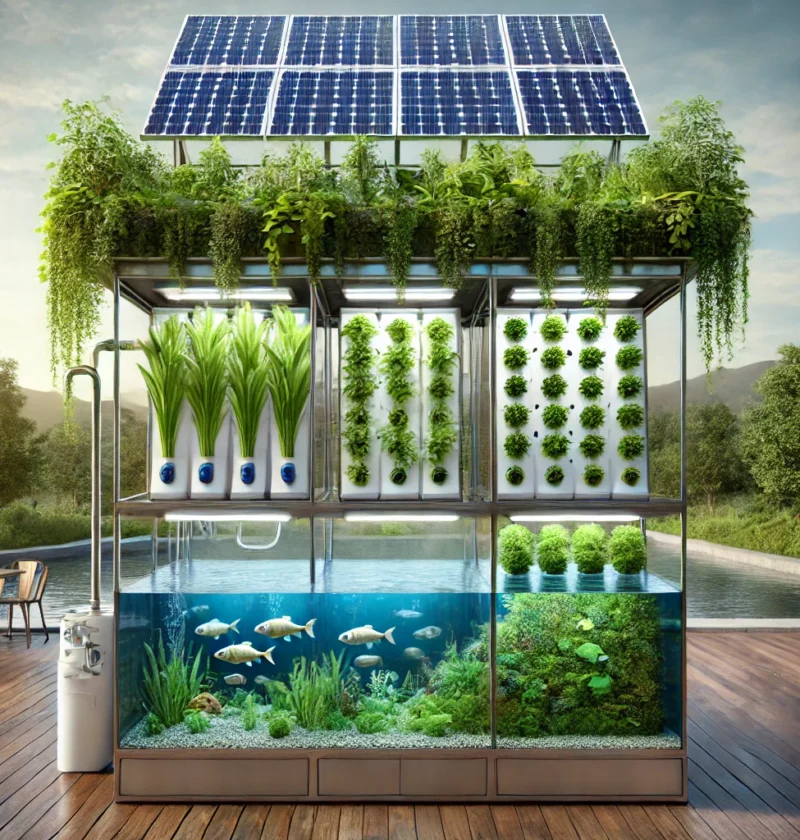
As the global population continues to rise, the demand for sustainable and efficient food production methods has never been more critical. One innovative solution that is gaining traction is solar-powered aquaponics—a system that integrates fish farming with vertical hydroponic plant growth. This closed-loop ecosystem maximizes space, conserves water, and reduces reliance on traditional farming practices. In this article, we will explore how solar energy enhances aquaponics, the key components of a successful system, and why this method represents the future of sustainable agriculture.
Understanding Aquaponics
Aquaponics is a symbiotic food production system that combines aquaculture (raising fish) with hydroponics (soilless plant cultivation). The fish produce waste, which, when broken down by beneficial bacteria, turns into nutrient-rich water that fertilizes plants. In turn, the plants filter and purify the water before it cycles back to the fish tank, creating an efficient and sustainable closed-loop system.
Key Benefits of Aquaponics
Water Conservation: Uses 90% less water than traditional soil-based farming.
No Chemical Fertilizers: The fish waste naturally enriches the plants, reducing the need for synthetic nutrients.
Efficient Land Use: Vertical hydroponic structures maximize yield per square foot, making it ideal for urban farming.
Fast Plant Growth: Nutrient-rich water accelerates plant growth rates, allowing for multiple harvests in a year.
Organic and Sustainable: No pesticides or herbicides are needed, leading to healthier food production.
Integrating Solar Power into Aquaponics
One of the key challenges of aquaponics is the energy demand for pumps, aerators, and lighting. By integrating solar energy, aquaponic systems can become fully self-sufficient, reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
How Solar Energy Powers Aquaponics
1. Solar Panels Generate Electricity: Photovoltaic (PV) panels capture sunlight and convert it into electricity.
2. Powering Water Circulation: The energy powers pumps that circulate water between the fish tank and the vertical garden.
3. Running Air Aerators: Fish require oxygenated water, which is maintained through aerators powered by solar energy.
4. Supplementary LED Grow Lights: In areas with limited sunlight, solar-powered LED grow lights can enhance plant growth.
5. Energy Storage with Batteries: Excess energy from the solar panels is stored in batteries, ensuring the system runs at night or on cloudy days.
Designing a Solar-Powered Aquaponics System
For a system to be effective and sustainable, several components must be considered:
1. Fish Tank
The fish tank holds aquatic life that produces organic waste.
Common fish choices: Tilapia, Catfish, Trout, and Goldfish.
Tanks should be made of non-toxic, food-grade materials.
2. Bio-Filter and Grow Beds
The bio-filter converts ammonia from fish waste into plant nutrients.
Grow beds support plant roots while allowing nutrient absorption.
Common crops: Lettuce, Basil, Kale, Tomatoes, Peppers.
3. Solar Panel System
Optimal wattage depends on system size (e.g., a 100W–500W system for small-scale setups).
Monocrystalline solar panels are recommended for higher efficiency.
Battery backup ensures continuous power during cloudy days.
4. Water Circulation System
Low-power DC pumps transport nutrient-rich water from the fish tank to plants.
Gravity-based drainage reduces reliance on electricity.
5. Automated Monitoring System
Sensors measure pH, temperature, and nutrient levels.
Smart controllers optimize water flow and aeration, reducing maintenance time.
Environmental and Economic Impact
Water Efficiency and Conservation
Traditional agriculture wastes nearly 70% of freshwater, whereas aquaponics recycles water continuously.
Rainwater harvesting can further enhance sustainability.
Reducing Carbon Footprint
Zero fertilizer runoff prevents pollution of natural waterways.
Lower transportation emissions as urban farms grow food locally.
Cost Savings Over Time
Initial setup costs may range between $500–$10,000, depending on scale.
Energy savings from solar panels make the system profitable in the long run.
Higher crop yields increase financial viability for urban farmers.
Challenges and Solutions
While solar-powered aquaponics offers numerous benefits, there are challenges:
Future of Solar Aquaponics
With advancements in solar panel efficiency, AI-powered monitoring, and automated irrigation, the future of aquaponics looks promising. Urban farms, schools, and even businesses are adopting small-scale systems to promote sustainable food production. Integrating vertical farming further maximizes space, making it ideal for high-density urban areas.
Conclusion
Solar-powered aquaponics is a game-changing solution for sustainable agriculture, combining fish farming, hydroponics, and renewable energy into a single, closed-loop system. This innovative approach conserves water, reduces carbon footprint, and increases food security, making it ideal for urban farmers, eco-conscious communities, and sustainable food enthusiasts.
🌿 Are you ready to build your own solar aquaponics system? Start today and be part of the future of food production! 🌍