Exploring Different Aquaponic System Designs: Sustainable Fish Farming and Hydroponic Plant Cultivation
Introduction: The Future of Sustainable Farming
In an era where sustainability is more critical than ever, aquaponics offers an innovative and efficient solution for food production. By combining fish farming (aquaculture) with hydroponic plant cultivation, aquaponics creates a closed-loop ecosystem that maximizes resource efficiency while minimizing waste. This highly sustainable method produces fresh vegetables and fish without the need for chemical fertilizers or excessive water consumption.
Aquaponic systems are gaining popularity among urban farmers, sustainable agriculture enthusiasts, and commercial growers due to their ability to produce high yields in small spaces. But what are the different types of aquaponic system designs, and how do they work? This article will explore the main aquaponic system designs, their benefits, and best practices for maximizing yield.
—
What Is Aquaponics?
Aquaponics is a symbiotic farming system that integrates aquaculture (raising fish) with hydroponics (growing plants without soil). The process revolves around the nutrient cycle, where:
1. Fish waste provides nutrients for plant growth.
2. Bacteria convert fish waste into plant-available nutrients.
3. Plants absorb the nutrients, purifying the water.
4. Clean water is recirculated back to the fish tank.
This system eliminates the need for chemical fertilizers and significantly reduces water consumption, making it a sustainable alternative to traditional farming.
—
Key Components of an Aquaponic System
To understand how different aquaponic system designs function, it is essential to recognize their key components:
1. Fish Tank
The primary source of nutrient-rich water.
Common fish choices include tilapia, catfish, trout, and goldfish.
2. Biofilter (Bacterial Colony)
Converts fish waste (ammonia) into nitrates, a form that plants can absorb.
Beneficial bacteria like Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter play a crucial role.
3. Grow Beds (Plant Cultivation Area)
Contains the plants that filter and absorb nutrients from the water.
Uses different growing methods, such as media beds, floating rafts, and NFT.
4. Water Pump and Pipes
Ensures continuous water circulation between the fish tank and grow beds.
Helps maintain oxygen levels and prevent stagnation.
5. Aeration System
Provides sufficient oxygen for fish and bacteria.
Essential for healthy fish growth and plant development.
—
Different Aquaponic System Designs
There are several aquaponic system designs, each suited for different plant types, available space, and investment levels. The three most common designs are:
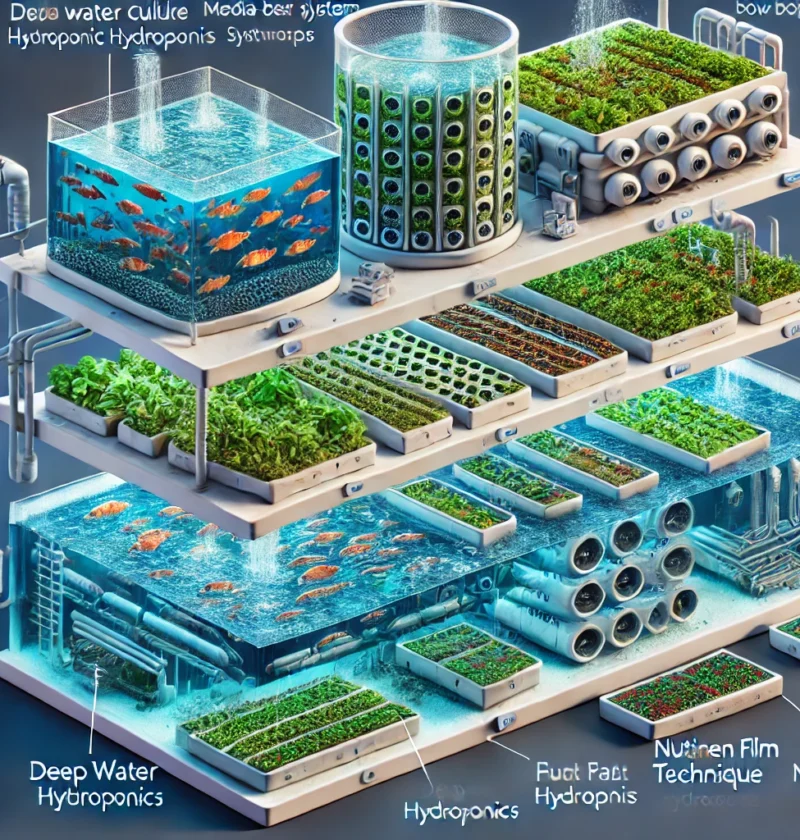
1. Media-Based Aquaponic Systems (Flood and Drain)
This is the most popular and beginner-friendly aquaponic system. It uses gravel, clay pebbles, or lava rocks as the growing medium, which supports plant roots while filtering solid waste.
How It Works:
Water from the fish tank is pumped into the media-filled grow bed.
The water floods the bed for a specific period, allowing plants to absorb nutrients.
Excess water drains back into the fish tank, preventing over-saturation.
Pros:
✅ Suitable for a wide range of plants (leafy greens, herbs, fruiting vegetables).
✅ Simple to set up and maintain.
✅ Excellent filtration of solid fish waste.
Cons:
❌ Requires periodic cleaning to prevent clogging.
❌ May not be ideal for large-scale commercial farming.
—
2. Deep Water Culture (DWC) / Floating Raft System
This design is widely used in commercial aquaponics because it supports high-yield production in a low-maintenance setup.
How It Works:
Plants are placed on floating rafts (usually made of styrofoam) above a deep water channel.
Nutrient-rich water continuously flows under the plants, supplying them with oxygen and nutrients.
Air stones or diffusers are used to oxygenate the water.
Pros:
✅ Ideal for leafy greens like lettuce, kale, and spinach.
✅ Highly efficient for large-scale food production.
✅ Requires minimal maintenance compared to media beds.
Cons:
❌ Not suitable for plants with large root systems (e.g., tomatoes, cucumbers).
❌ Requires aeration equipment to prevent root rot.
—
3. Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) Aquaponics
The NFT method is commonly used for growing small plants and herbs in a space-efficient manner.
How It Works:
Water flows continuously through narrow channels or pipes.
Plant roots hang into the shallow stream of nutrient-rich water.
Water drains back into the fish tank after nutrient absorption.
Pros:
✅ Uses minimal water, making it highly efficient.
✅ Perfect for small plants like basil, mint, and strawberries.
✅ Ideal for vertical and urban farming.
Cons:
❌ Not suitable for large plants with deep root systems.
❌ Risk of system failure (e.g., pump malfunction can dry out roots quickly).
—
Which Aquaponic System Is Best for You?
Choosing the right aquaponic system depends on several factors, including space availability, plant types, and budget.
For beginners, a media-based system is the best option due to its simplicity and versatility. Commercial growers often prefer DWC because of its high production capacity, while NFT is great for compact spaces.
—
Benefits of Aquaponic Farming
Aquaponics offers several advantages over traditional soil-based farming and conventional hydroponics:
✔️ Water Conservation – Uses 90% less water than soil farming.
✔️ No Chemical Fertilizers – Natural fish waste supplies nutrients.
✔️ Higher Yield in Less Space – Ideal for urban and indoor farming.
✔️ Minimal Waste – Closed-loop system recycles nutrients.
✔️ Sustainable and Eco-Friendly – Reduces environmental impact.
—
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While aquaponics is highly efficient, it comes with challenges:
1. Maintaining Water Quality
Solution: Test pH, ammonia, and nitrate levels regularly to ensure a balanced ecosystem.
2. Choosing the Right Fish
Solution: Select hardy fish like tilapia, goldfish, or trout, depending on your climate and system setup.
3. Managing Plant Growth
Solution: Match plant selection to nutrient availability, focusing on high-yielding greens and herbs.
4. Preventing Disease
Solution: Ensure good water circulation, adequate aeration, and proper sanitation to prevent bacterial growth.
—
Conclusion: The Future of Sustainable Farming
Aquaponics represents the future of sustainable agriculture, offering an eco-friendly, efficient, and high-yield farming method. Whether you are a home gardener, urban farmer, or commercial grower, integrating fish farming with hydroponic cultivation allows you to produce fresh vegetables and fish year-round while conserving resources.
Call to Action
Ready to start your own aquaponic system? Choose the right design for your space and experiment with different plant-fish combinations for optimal growth. Happy farming! 🚀🌱🐟